SLS – Selective Laser Sintering
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a form of additive manufacturing technology under the powder bed fusion technique category. SLS is primarily associated with printing plastic parts and components. The parts are built by fusing material with a laser, a fine-grained powder, layer by layer. The process takes place in a high temperature inside the printers build chamber that is protected with inert nitrogen gas to prevent oxidation.
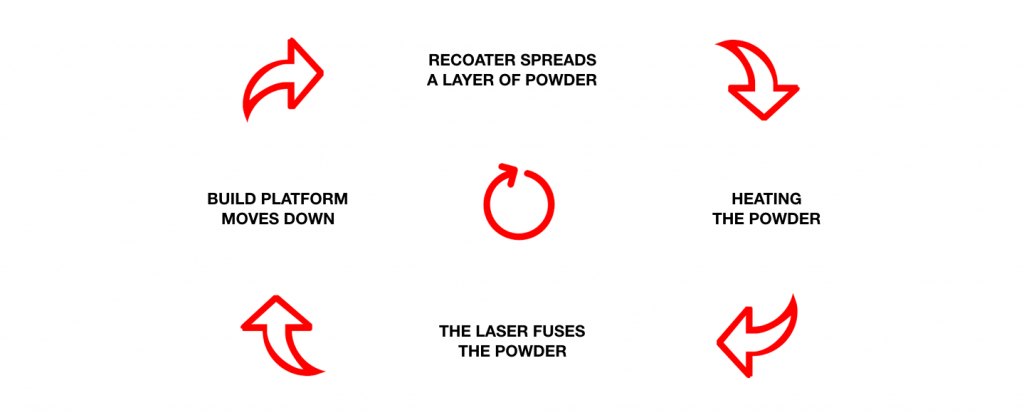
In essence, the laser fuses the powder into a desired form. The production machine spreads an even layer of powdered plastic on the build platform inside the build chamber. The powder is then fused by the laser. When the form is ready the production machine lowers the build platform according to the layer thickness and spreads a new layer of powder which is again fused by the laser. The process is repeated until the parts are ready. The surrounding excess powder supports the parts during fusing so the final outcome is a “powder cake” with the parts inside. When the process is done the excess powder is removed, sieved, recycled, and the finished parts will go through post processing procedures. SLS allows efficient production runs and intricate geometries but the finished parts surface quality is moderately rough. The surface quality can be improved with different post processing techniques such as vibratory finishing.

Print materials
The most common raw material for SLS is a PA12 based nylon. At Materflow we use a white and black colored version of PA12. The material’s mechanical properties are well suited for industrial use: it’s extremely durable, flexes well before breaking, and has a high chemical resistance. These qualities make PA12 one of the best 3D printing polymers for end-use parts. There are also different mixtures of PA12 available. Adding small glass beads to the mix gives the material some stiffness and heat resistance. With SLS it’s also possible to print elastomers such as TPU.
PA12 Glass Fill (GF) – PA12 with small glass beads. Slightly stiffer and with better heat resistance than pure polyamide. The color is off-white/beige.
TPU – Thermo plastic polyurethane. TPU based material, high performance. Excellent mechanical properties, impact resistance, and elongation. It’s also a very flexible material.
These are the main plastic materials we use at Materflow. There are many other materials available for SLS technology but they usually require alterations to the machines configurations or other special components for production. Other materials include PP, PA6/6, PEKK, PEEK, and polystyrene. PA12 powder has also several color and additive variations.
Key components for printing machines
SLS printing machines are very reliable and produce accurate parts. The machines are primarily for industrial use with a long lifespan (10-20 years). They have a modular setup which makes it easy to perform maintenance and update the key components when needed.

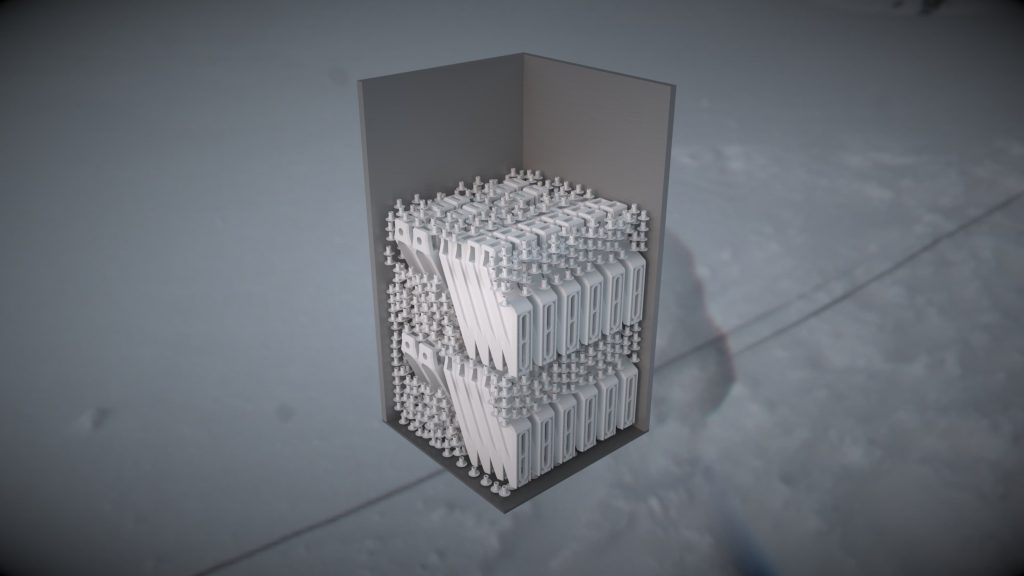
The printed parts are optimised into the build chamber before printing.
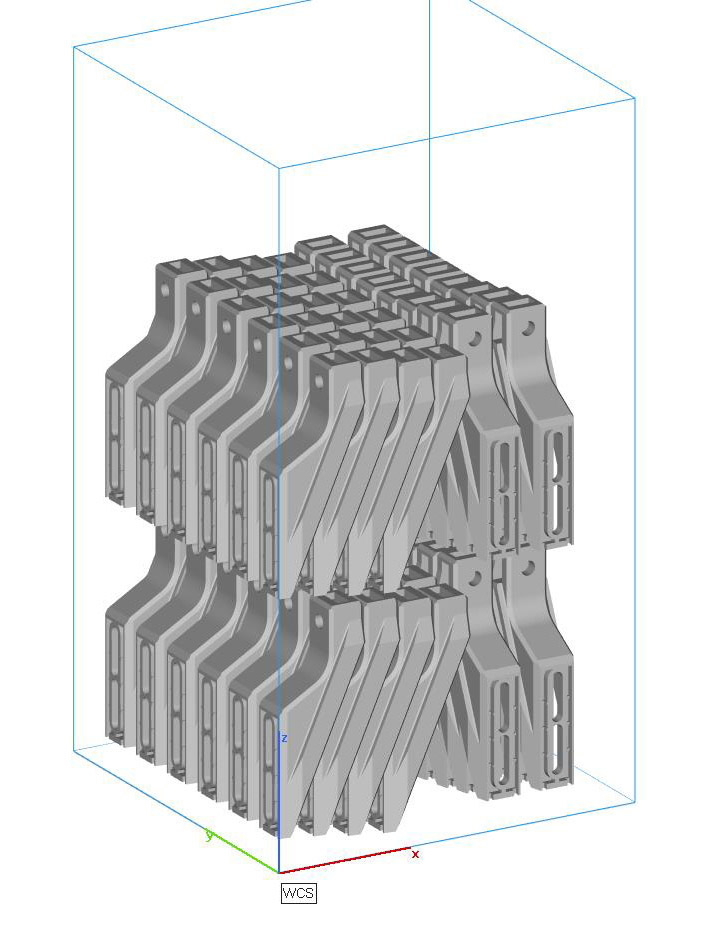
The better the optimisation, the better the capacity for a producion run.
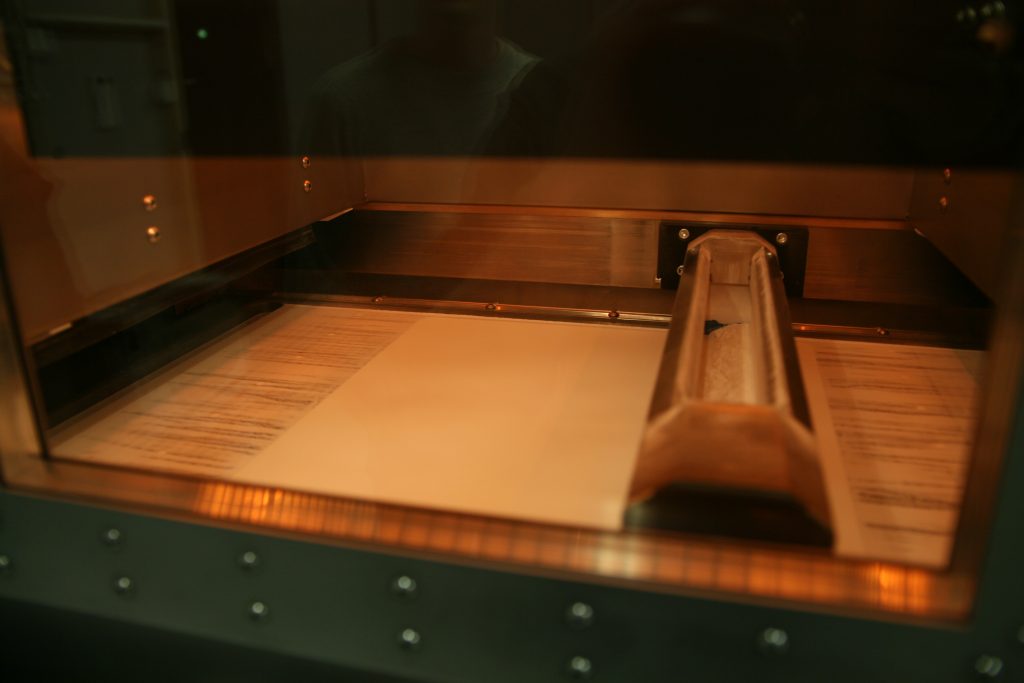

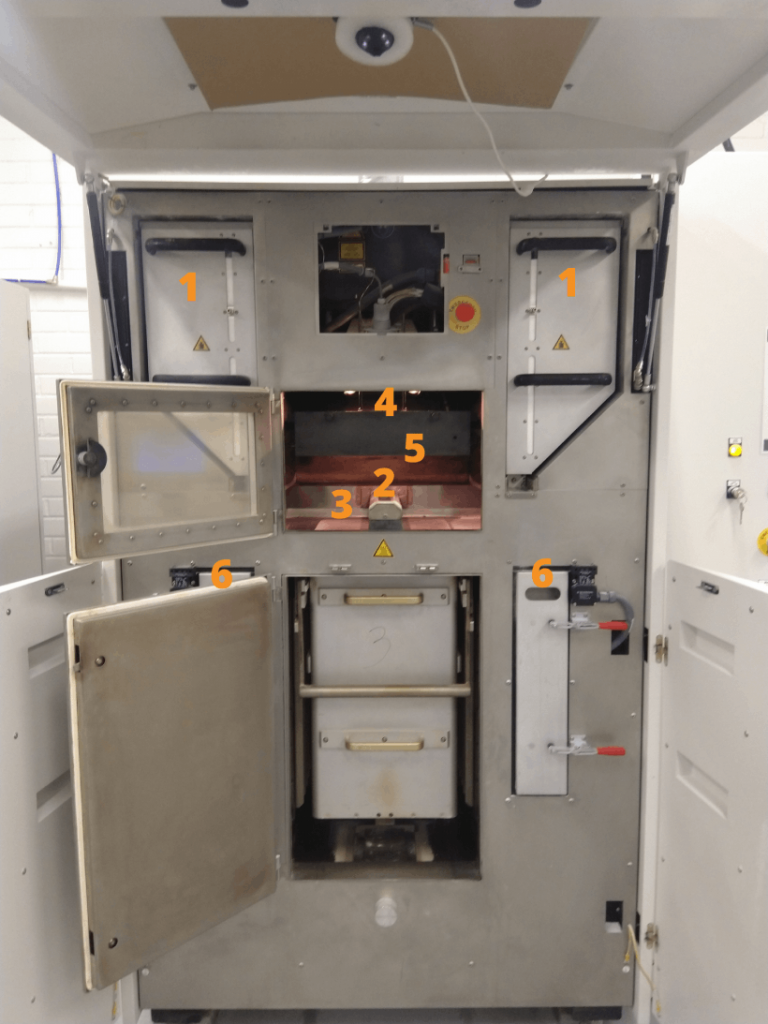
1. Material feeds – The powdered material is deposited through the material bins that dispense the powder for the recoater. The recoater spreads the powder evenly on the build platform.
2. Recoater – In general there are two types of recoaters: a blade or a counter-clockwise turning roller. With both types you can setup and control the density of the powder bed. The density affects how the parts form and if the powder is packed too densely on the build platform by the recoater it’s harder to remove the finished parts from “the powder cake” and other excess powder.
3. Build platform – The parts form on the build platform. The platform is inside a sealed build chamber so that the temperature remains steady (120-130 degrees Celsius). When a build starts the platform is at its uppermost level. When a layer is done the platform moves slightly downwards so that the recoater can spread a new layer of powder. A typical layer thickness varies between 0.1-0.15mm. The build platform and build chamber dictates the max size for printed parts. A well sealed build chamber prevents the parts from warping since it also allows a steady cooling process. Our build platforms at Mateflow are exchangeable units which means they can be removed from the build chamber after printing to perform the cooling process elsewhere, and load a new production run with another build platform instantly.
4. Laser and salvos – Above the build platform is a laser that fuses the powder layer by layer. A two-mirror system directs the laser precisely as needed. Power and speed can be adjusted to achieve optimal outcome. The beams distortions are compensated with a F-theta lens which allows accurate builds on a large surface.
5. Build chamber – Build platform, thermal sensors and heaters, laser window, optics, pyrometer and recoater are all inside the sealed build chamber.
6. Overflow bins – All the excess material from each recoating round ends up in the overflow bins. The excess powder from the bins can be reused as is since it hasn’t been exposed to high temperatures.
Other equipment – The SLS process requires an inert atmosphere which is achieved with a nitrogen generator. The generator maintains a low oxygen level to prevent oxidation. Also different equipment and procedures for post processing are important for removing and recycling the excess powder and improving the parts surface quality.
SLS process
The process starts with pre-heating the printing machine for 2-3 hours. Inert atmosphere is created by inserting nitrogen into the build chamber. After pre-heating the recoater spreads the powder on the build platform. When a desired temperature is reached the laser starts fusing the powder. When the layer is done the recoater spreads another layer of powder and the laser fuses. This process is repeated until the production run is done.
After the production run the powder cake is slowly cooled down to room temperature. If cooled too fast some warping might occure on the finished parts. After cooling the excess powder is removed, collected, and sieved for reuse. The sieved excess powder is mixed with new powder according to the manufacturers instructions. The portions depend on the material in question. Normally 50% of new powder is needed but in case of fire rated materials only new, unused powder is allowed for production runs in order to achieve wanted standards.
SLS printed parts are both strong and durable. At Materflow we use printing machines designed and built by the German EOS Gmbh. With EOS printers it is easy to duplicate and repeat production runs or perform runs as needed. The capacity and efficiency of the machines enable optimised and accurate production runs and mass production.
Common usage
Prototypes – SLS is a cost-effective technique to produce fully functional prototypes with all moving parts. It is generally used to build demo products for new concepts and to validate first article pieces on production or design standpoint. Because of the techniques rapid and versitaile production capabilities designers and product developers can easily materialise different iterations to validate and develop the product or concept.
Iterative design – To quickly validate iterations with physical models makes the whole design process more effective. It also frees up time for developing functionalities and design.
Spare parts and discontinued parts – In principle 3D printing is a faster and more cost-effective way to produce spare parts and discontinued parts than conventional methods, especially with low volume production.
End use applications – In general end use applications have many requirements when it comes to design details, build tolerance and material properties. SLS technique and materials can match these requirements offering a precise and firm option as a production method for end use applications. E.g. nylon based prints can be produced with an utmost preciseness, typically within +/- 0.125mm accuracy per direction. Other advantages with nylon: high impact strength, moderate flexibility, high resistance for harsh environments (e.g. high and low temperatures), water-tight applications, good chemical resistance and long lifespan with outdoor usage.
Post processing
Dyeing – Parts printed with SLS are in principle white or slightly yellowish depending on the material. With dyeing parts are available in all primary colors and in some other shades as well. The end result with dyeing is very durable and of high-quality. Dyeing with submergence gives the parts UV protection. With submergence the color is saturated into the part in a high temperature. This ties the color to the part chemically and gives resistance against most solvents. Depending on the material the color makes a layer about 0.2-0.4mm.
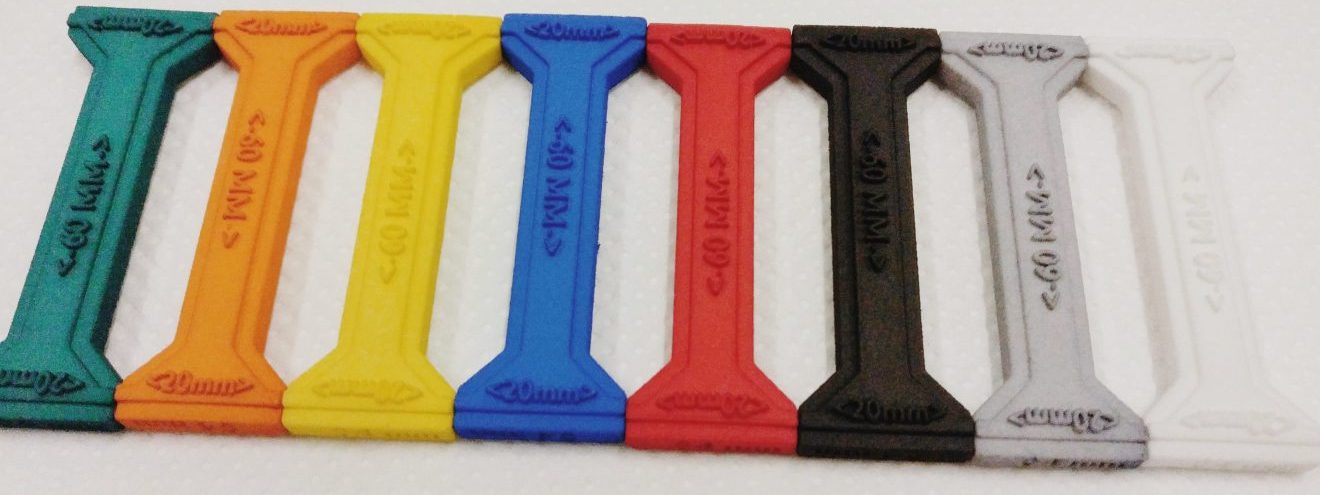

Tumbler finishing – Finished prints are slightly rough on the surface. This is due to the particle size of the recycled powder which partly melts on the top layers. The surface quality can be improved with tumbler finishing. After the process the surface quality is close to that of an injection moulded part. The dimensional accuracy suffers only about -0.1mm and sharp corners and edges are affected the most giving them a slightly rounded profile. These losses can be handled by optimising the model before printing. If dyed after tumbler finishing the parts surface quality is improved even more.

Want to know more about SLS or have a project in mind? Contact us for more information


